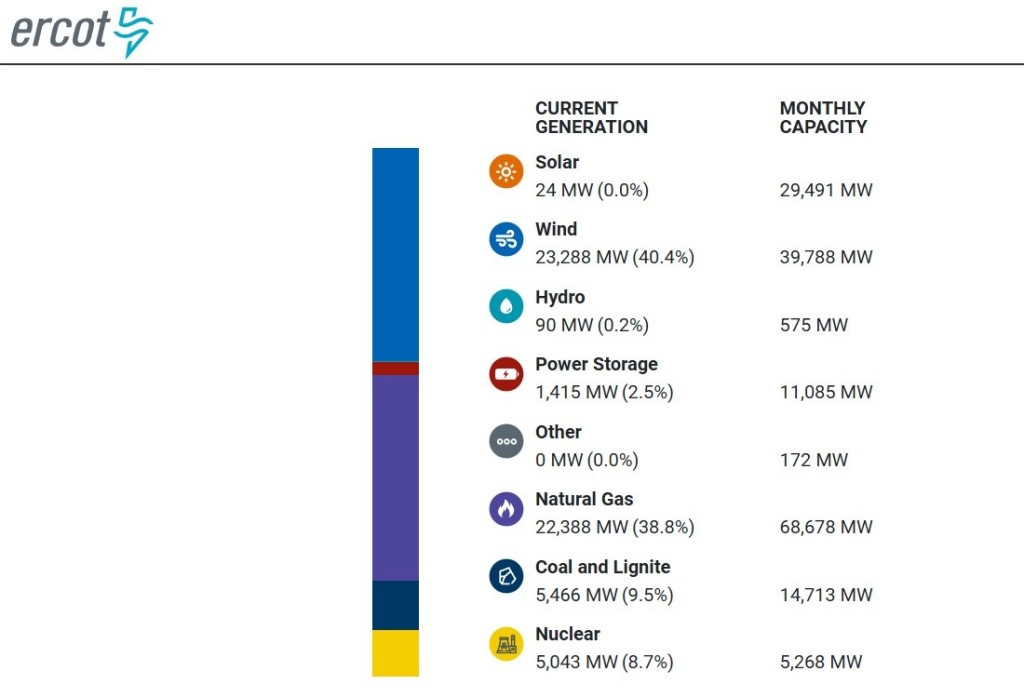
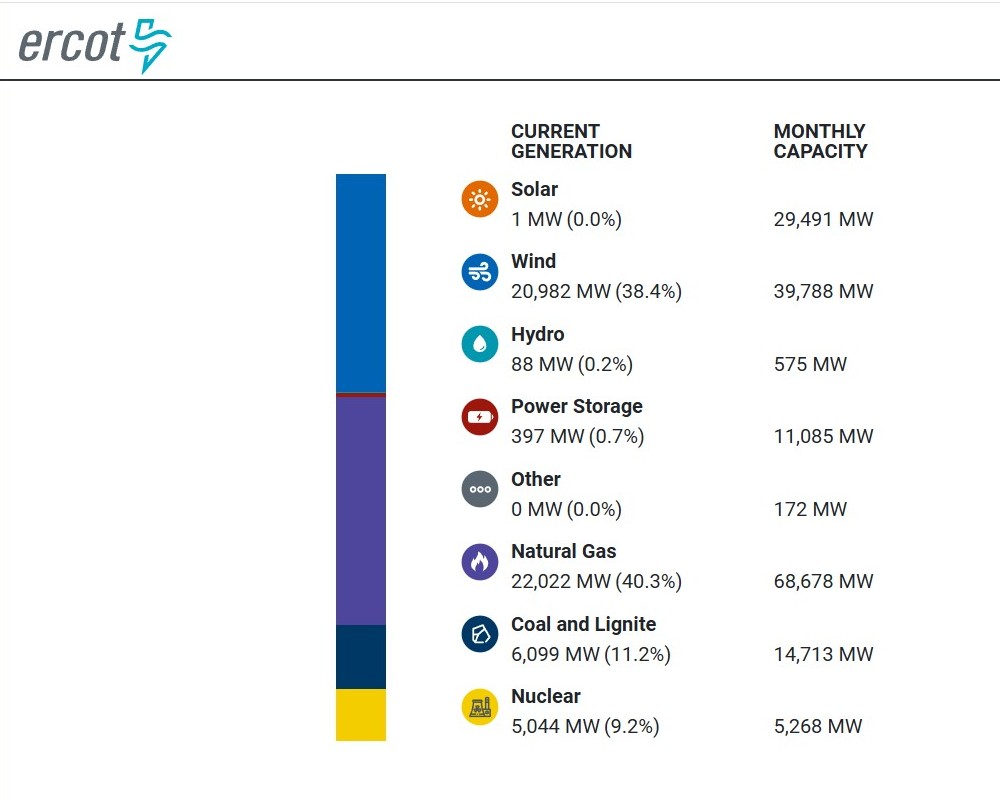
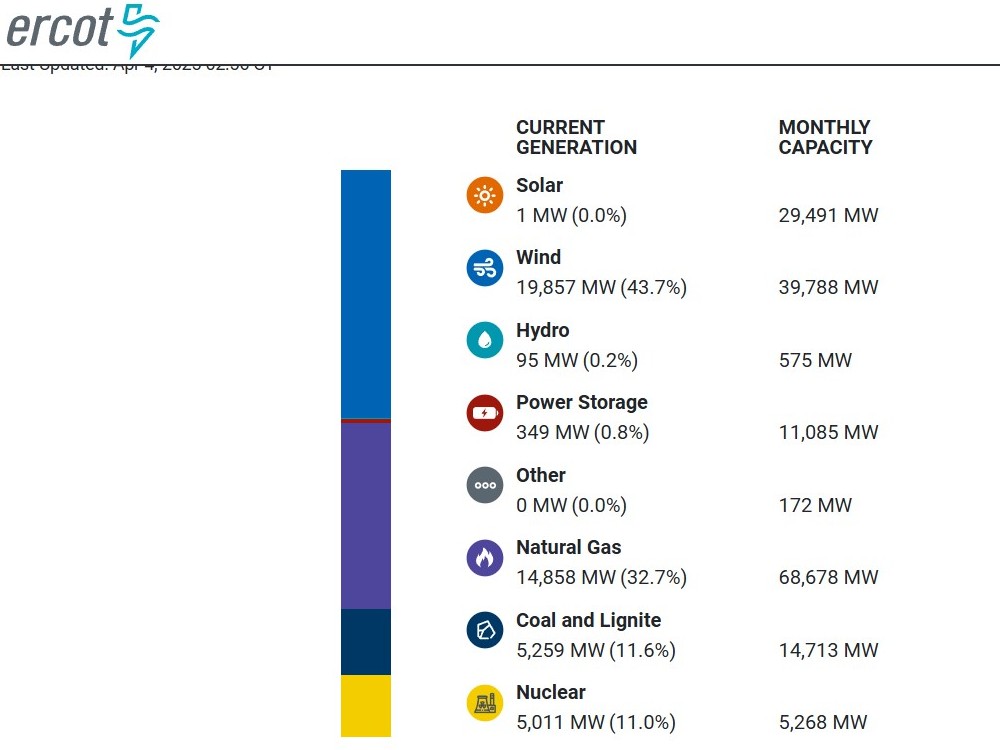
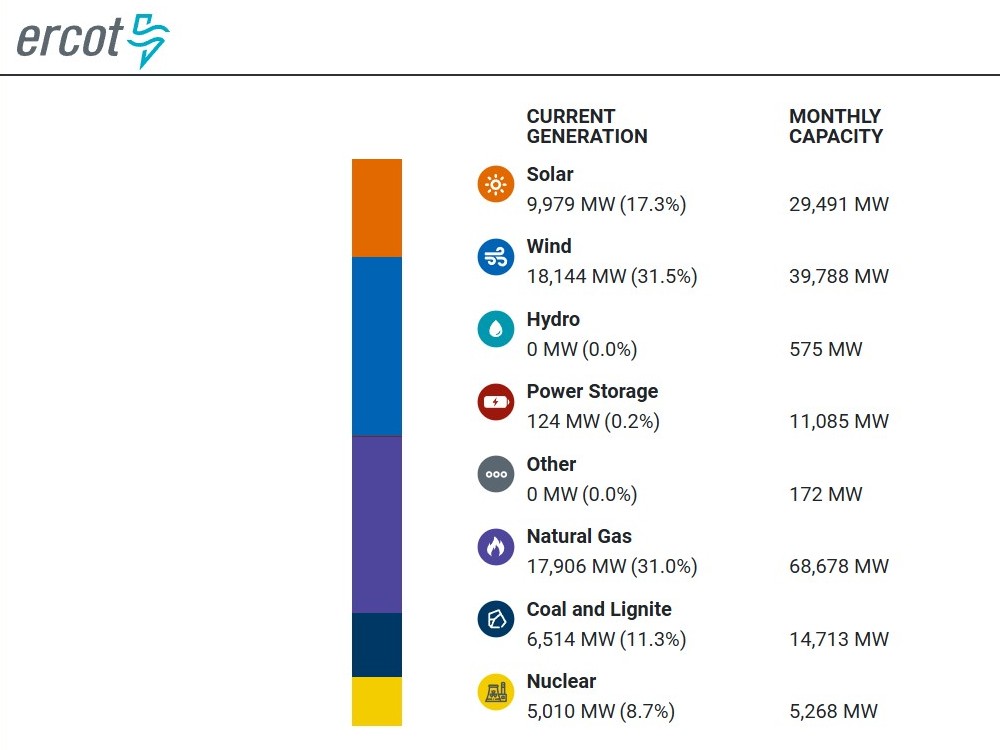
Super fact 39 : Relativistic length contraction goes both ways. If two observers are moving compared to each other both will observe the length of the objects in the other’s system to be shorter in the direction of motion. The first observer will think that a yard stick in the second observer’s frame will be shorter whilst the second observer will think that the yard stick in the first observer’s frame is the shorter one.
Assume a pole and a barn are of equal length when both objects are stationary. If the pole is moving (at a high speed) compared to the barn, then the pole will be shorter than the barn from the barn’s perspective but longer than the barn from the pole’s perspective. Does the pole fit inside the barn or not? This is referred to as the pole-barn paradox, or the barn-door paradox, or the ladder paradox (if a ladder is used instead of a pole).
I call this conundrum a super fact because whilst most people have heard of relativistic time dilation and perhaps length contraction, the fact that it goes both ways comes as a surprising head scratcher. The situation is analogous to my super fact post “Time Dilation Goes Both Ways” where I state:
Super fact 38 : If two observers are moving compared to each other both will observe the other’s time as being slower. In other words, both observers will observe the other’s clocks as ticking slower. Time slowing down is referred to as Time Dilation. And this post is about how time dilation goes both ways.
Both the time dilation paradox and the pole-barn paradox are solved by the non-simultaneity in relativity. However, the pole-barn paradox is more concrete and perhaps more in your face. You can easily imagine the problematic paradox.
Postulates of Special Relativity
The two postulates of special relativity are:
- The laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames of reference. An inertial frame is a system that moves at a constant velocity.
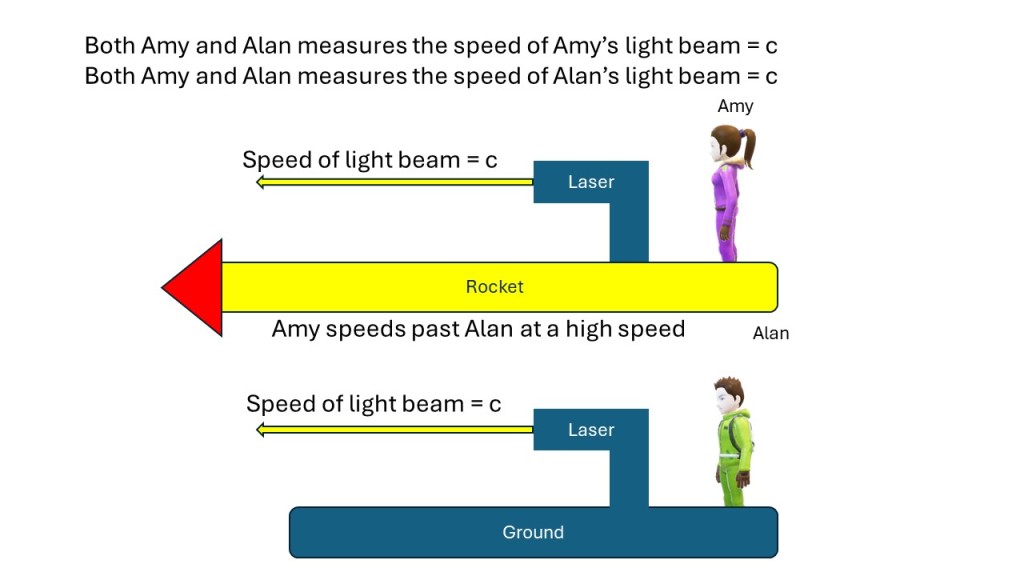
- The speed of light in a vacuum is constant for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source.
The first postulate is called the principle of relativity and goes all the way back to Galileo Galilei. It means that no experiment can determine whether you are at rest or moving at a constant velocity. The reciprocity of length contraction follows from this postulate. If the length of the pole in the example above is half as long as the barn in both the barn frame and the pole frame then you could tell who was standing still and who was moving from that fact, and that violates the first postulate. The first postulate demands that if the pole is half as long in the barn frame and that the barn is half as long in the pole frame.
The second postulate is the more shocking one and is special to relativity. It was discovered experimentally at the end of the 19th century but was too difficult for scientists to accept at first so various ad hoc explanations were put forth to explain it away, until the theories of relativity were created. I designated this postulate as my super fact #4 and you can read about it here.
Length Contraction
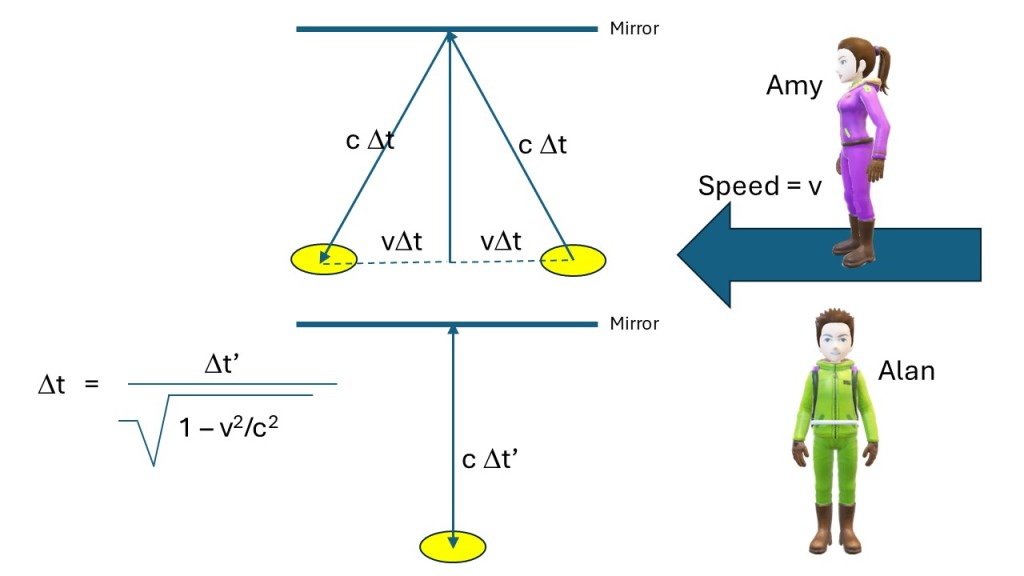
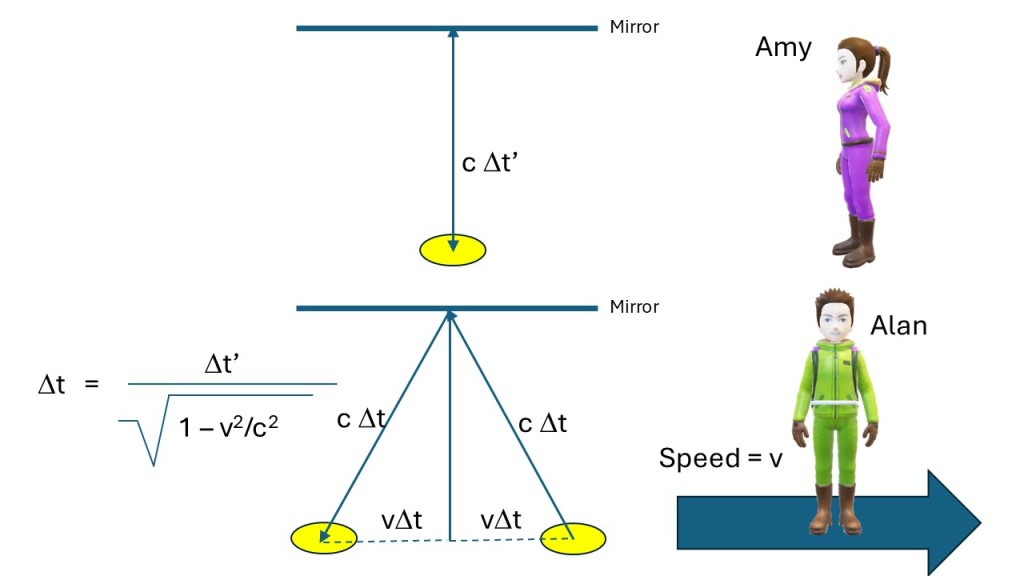
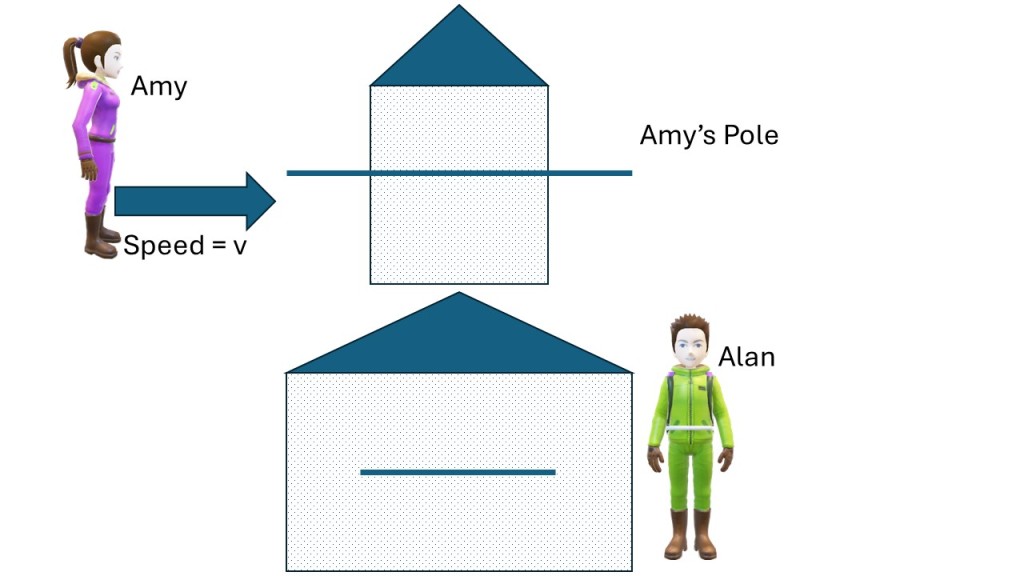
Time dilation means that a time interval between two events in a certain frame is longer by a factor B in a frame moving relative to the first frame (see picture below). Let’s imagine Amy moving at the speed v compared to Alan and his barn. Amy passes the left side of the barn at a certain time and soon after the right side. The time difference from Alan’s perspective is T and the width of the barn is L, so L = vT. From Amy’s perspective the time difference is T’ and width of the barn L’ and L’ = vT’. We denote Amy’s measurements with a prime. Note the velocity must be the same in both systems. However, Amy’s clock ticks slower (from Alan’s perspective) so T’ = BT or T = T’/B (time dilation). So, L’ = vT’ = vT/B = L/B.
If the derivation of the formulas above is confusing to you, ignore the math, and just remember that Alan measures a shorter time for the passing of the pole (because Amy’s clock is slower) from his perspective and therefore the pole must be shorter as measured from his system. If Alan measures two seconds for the passing of the pole than Amy measures maybe four seconds. It is Amy’s pole, so her longer measurement corresponds to the proper length of the pole whilst Alan’s measurement is the contracted length. Note the length contraction can only happen along the direction of motion, not perpendicular to it. To read more about length contraction click here.

Solution to the Pole-Barn Paradox
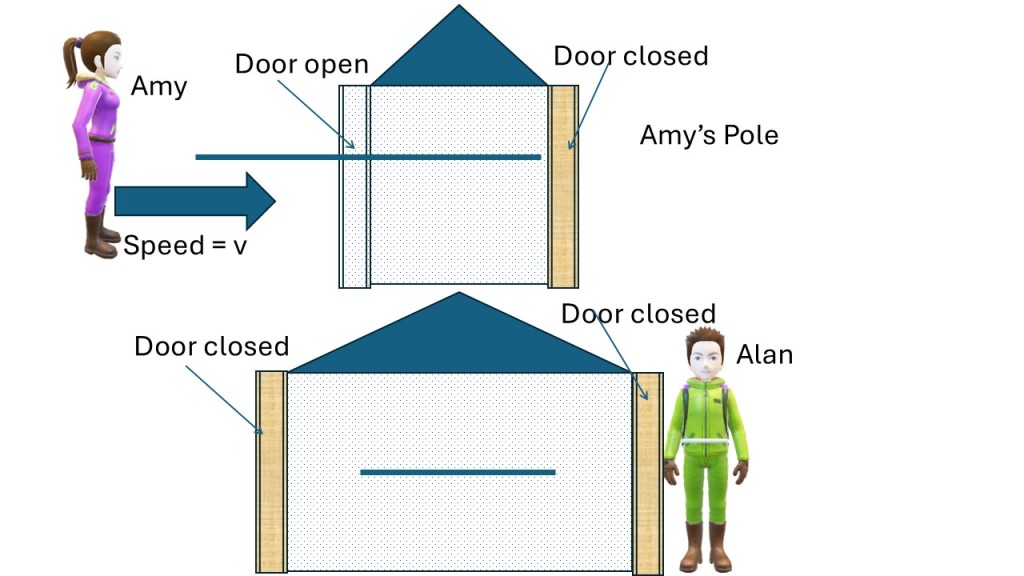
So, Amy’s pole cannot fit in Alan’s barn. The pole is moving fast so it must move in and out of the barn. Now let’s create the paradox. Imagine the barn having doors on each side that open for the moving pole and then close for a moment to entrap the pole and then they open as the pole leaves the barn. Here is the paradox, if they open and close at the same time, than the pole can be inside the barn (entrapped) from Alan’s perspective but not from Amy’s perspective. From Amy’s perspective the pole does not fit.
However, the solution to the paradox lies in “open and close at the same time”. If the doors open and close at the same time from Alan’s perspective, then they don’t open and close at the same time from Amy’s perspective.
From Amy’s perspective the door on the left side will open first and let the pole in and then after that the right door will open. After the pole has fully entered the barn and some of it is sticking out on the right-hand side then the left door will close but the door on the right will remain open until the pole is entirely outside. Relativistic non-simultaneity solves the paradox.
Finally, below is a YouTube video that explains and solves the pole-barn / barn-door / ladder paradox simply and efficiently in a little over two minutes.
Book Recommendations on Relativity
- Relativity Visualized by Lewis Carrol Epstein. This book does not require much education in physics and very little math, and yet it explains relativity very well.
- Relativity, The Special and the General Theory, by Albert Einstein. In my opinion, not the best overall, but it is easy reading for the public and the chapter on the relativity of simultaneity is pretty good.
- Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei and Particles by Robert Eisberg and Robert Resnick. An advanced but excellent explanation of special relativity in the appendix.
- The Special Theory of Relativity by David Bohm. It is written for people with some physics education. However, it is one of the best books on Special Relativity that I’ve read.
- Einstein’s Miraculous Year. This book features the translations of the five famous papers that Albert Einstein wrote in 1905 including “On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies”, which was his paper on Special Relativity. Not for the faint of heart but very interesting.