This post is not a super fact post but it contains some other important information. 23AndMe, the large personal genomics and biotechnology company just went into bankruptcy. This has implications for its 15 million customers including me and my wife. In fact, it is advised that you delete your data from their website, and I will tell you how to do that.
About 23AndMe
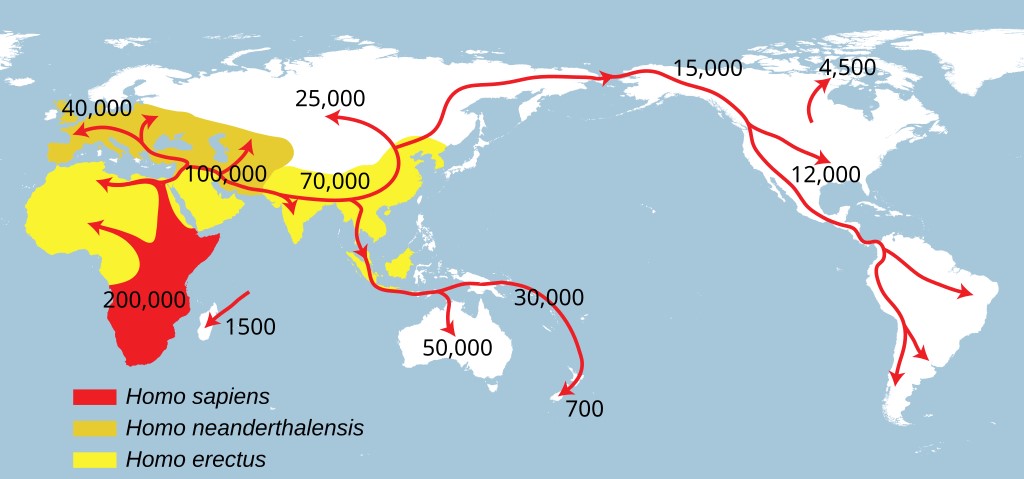
23AndMe, founded in 2006 provides a direct-to-consumer genetic testing service in which customers provide a saliva sample that is analyzed to generate reports relating to the customer’s ancestry, genetic predispositions, inherited health conditions and other health related topics. Who doesn’t want to know something about their ancestry going back possibly thousands of years? Who doesn’t want to know about genetic timebombs in their DNA? I took the test, and my wife took the test, our daughter took the test, other family members took the test, and it was fun and very interesting, and a good conversation starter. For example, I found out that I am practically a Neanderthal, well maybe not exactly.

What we did not think about is that 23AndMe represented a significant privacy risk. This is data that can be misused in various ways. You can be discriminated against based on this data, you can be denied employment, insurance companies can use it to deny you health insurance, you can be subject to surreptitious testing without your consent. Not to mention familial complications, such as infidelity, and people finding out who their real parents are, and relatives were. In the wrong hands this data is dangerous.
In October 2023 hackers stole 7 million people’s data. Stolen information included people’s names, addresses and genetic data and was sold online. This made the economic difficulties the company was in even worse. Yesterday the company filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy and their founder and CEO resigned. Now people are rightfully worried about their data.
Ancestry from 23AndMe
However, the information we got from our genetic tests was interesting and fun. I found out that my ancestry was 99.8% Northwestern European, 85.3% Scandinavian/Sweden/Norway, 14.4% Finnish, 0.1% other Northwestern European, and 0.2% Siberian. Not surprising since my family have lived in northern Sweden and northern Finland since at least 1628 according to the ancestry records. Other people in my family were a lot more mixed than that. I can add that I also thought it was fun to on occasion find second cousins or third cousins whose existence I was unaware of.
I also found out that I had strong Neanderthal ancestry. The report says I have more Neanderthal variants than 99% of customers. On the 23AndMe website there was a forum, or club for people with strong Neanderthal ancestry, so I joined. However, some people were taking it a bit too seriously and after I while I did feel comfortable in the Neanderthal club, so I left.

Fun Facts from 23AndMe
I was happy to find that I did not seem to have any hereditary predisposition for any illnesses among the ones they listed. Well, I have the typical predisposition for type II diabetes. I was happy to see that I am not predisposed to get Alzheimer’s, which I was worried about, since I have a couple of relatives with that condition.
The most fun and perhaps least important aspect of the genetic testing was the non-health related predispositions. For example, regarding “ice cream flavor preference” my genes says that I am “more likely to prefer vanilla over chocolate ice cream”. My wife got the opposite, and this is correct. I love vanilla, she loves chocolate. I am less likely than average to be afraid of heights and less likely to be motion sick.
Our eye colors, finger and toe lengths, propensity for dandruff, cheek dimples, hair texture and thickness, earwax type, freckles, bunions, the DNA analysis got it all right. By the way I am good at smelling asparagus, just like my DNA test says. The one thing that my DNA test got wrong was that the most likely time for me to wake up in the morning is 6:53AM. The DNA test got my wife’s wake up time correct, but I am not waking up at 6:53AM.
Deleting your data from 23AndMe
OK this is a lot of fun and maybe useful, but the big question is do we want this information in the wrong hands. I’ve mentioned a few ways in which this data can be misused but there may be many more ways this data can be misused that I have not thought about, that no one has yet thought about. Therefore, I deleted all our data from 23AndMe today. If you are a member of 23AndMe I suggest you do the same. Below I am giving you the instructions for how to delete your data from 23AndMe.
- Log into your 23andMe account. You may need to reset your password.
- Go to your profile and locate the little menu up on the far top right. Select Settings.
- Scroll to the “23andMe Data” section at the bottom of the page and click View (button). If you want to download your data, select what you want to download. I downloaded the “reports summary”, which is a pdf file. I also downloaded ancestry composition raw data, which is a large CSV file compressed into a zip file. Finally, I downloaded family tree data, which is in json format.
- Scroll to the “Delete Data” section and click Permanently Delete Data. This is a Red button at the bottom.
- Confirm your request: You’ll receive an email from 23andM. Click the link/button in the email to confirm.
Important Note : I am back from my ski vacation, and I once again respond to comments posting and visiting other people’s blogs.