Super fact 33: Actions such as eating locally, buying organic produce, using paper straws, and recycling can be good for the environment but can also be worse for the environment and these actions often have a much smaller positive impact than alternative rarely considered actions. What are popular actions for the environment is often different from what is effective.
I consider this a super fact because the beliefs regarding what is good for the environment and what is bad for the environment and what has a significant impact and what has not, are often based on popular trends and culture rather than knowledge. We need to educate ourselves. Following trends is not the answer to good stewardship of the planet.

Is Locally Grown Food Really Better for the Environment?
As I explained in this post eating locally is not necessarily ecological. Agricultural products that are grown off season or in non-native environments are often grown in greenhouses, which require a lot of energy and generate significantly more emissions than shipping the produce across oceans would. This is especially true for crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, mangoes and bananas, that require warmer climates to be grown in open fields.

In some cases, the crop requires significant water resources or chemical inputs to thrive and may not be suitable for warmer climates, for example, apples. Some crops, like avocados or almonds require a lot of water but despite that they are grown in dry places like California (80% of California’s freshwater is used for agriculture). From an environmental perspective it would be better to grow these crops in a suitable environment and then transport them.
Is Eating Organic Really Good for the Environment?
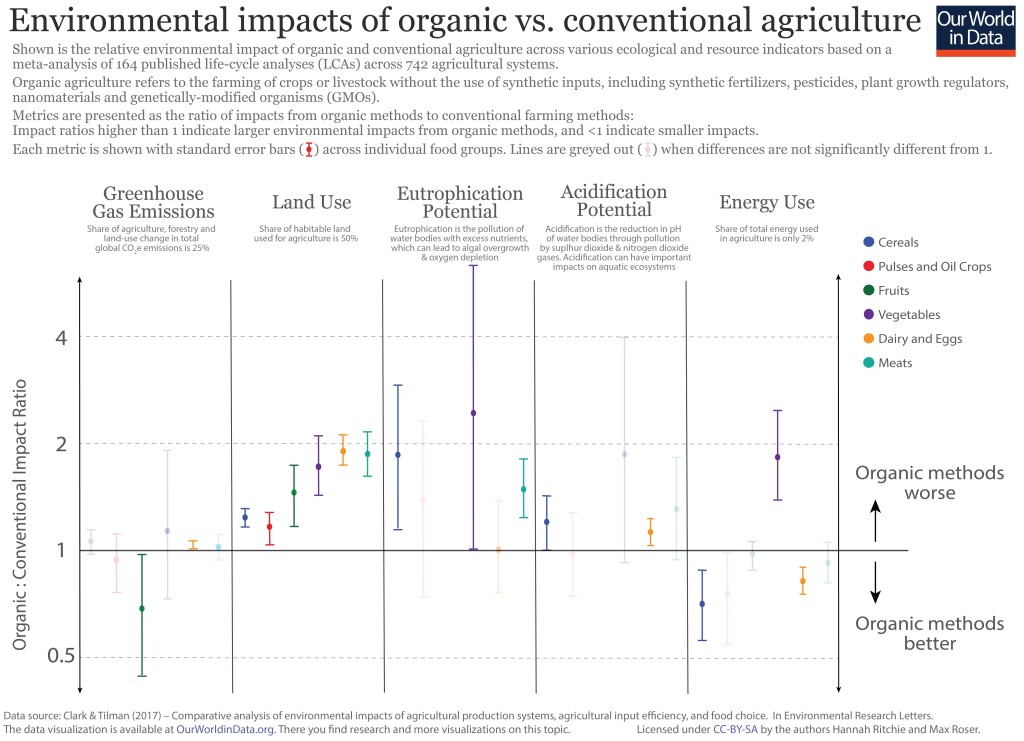
As explained in this post eating organic is not necessarily ecological. Despite strong public perception of organic agriculture producing better environmental outcomes, conventional agriculture often performs better on environmental measures including land use, greenhouse gas emissions, and pollution of water bodies. There are, however, some contexts where organic agriculture may be better for the environment.
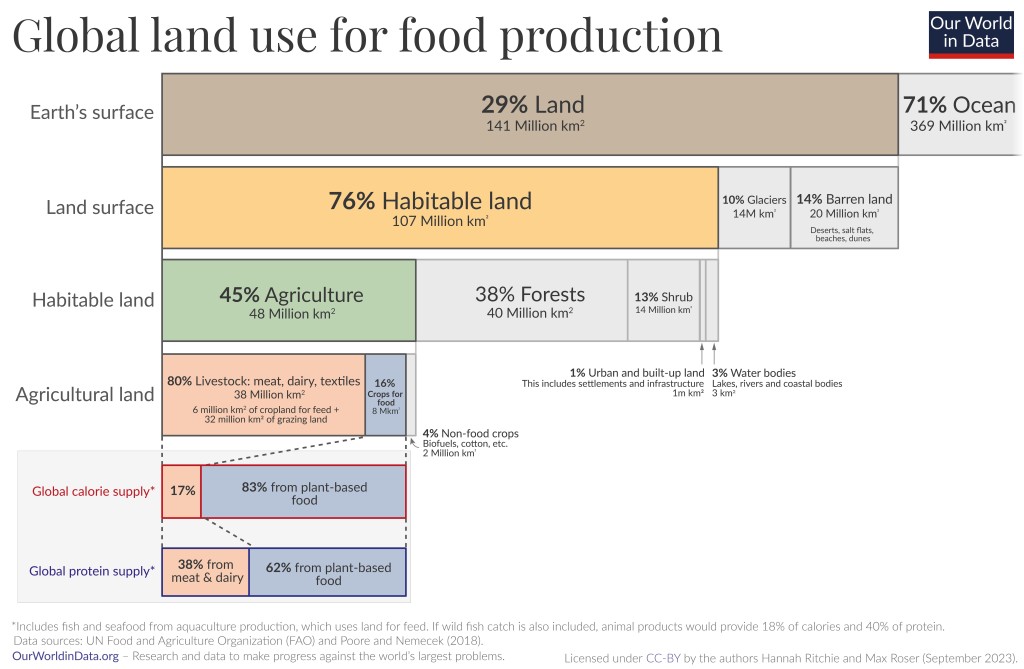
The graph below gives an overview of the environmental impact of various types of crops grown organically and conventionally. As you can see organic crop often require double as much land compared to conventionally grown crops. It is complicated.
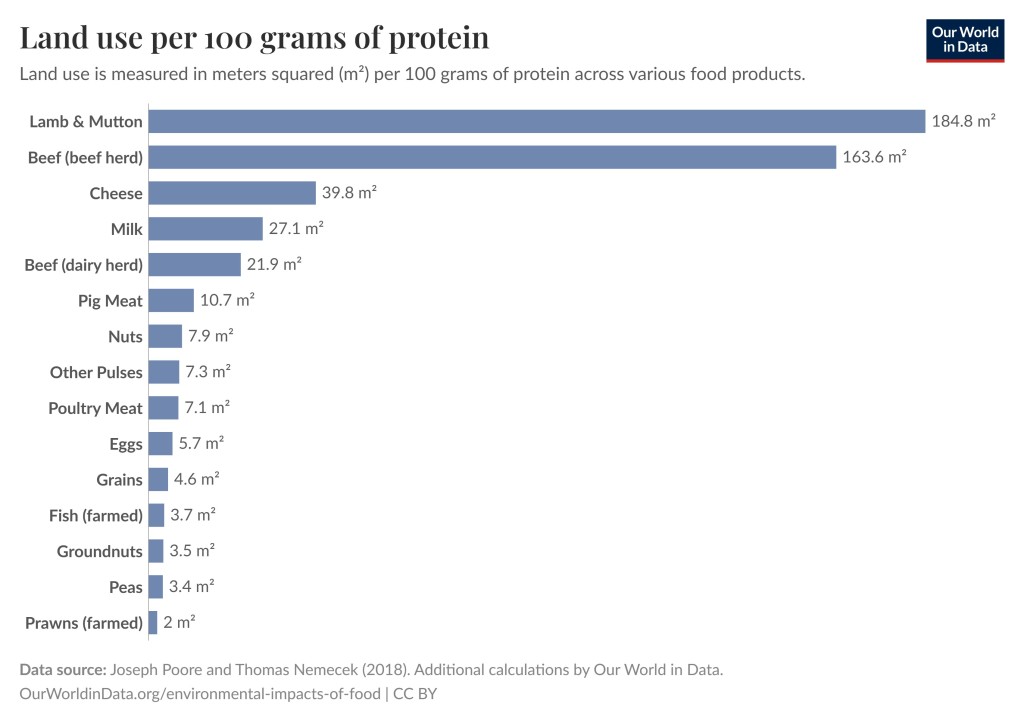
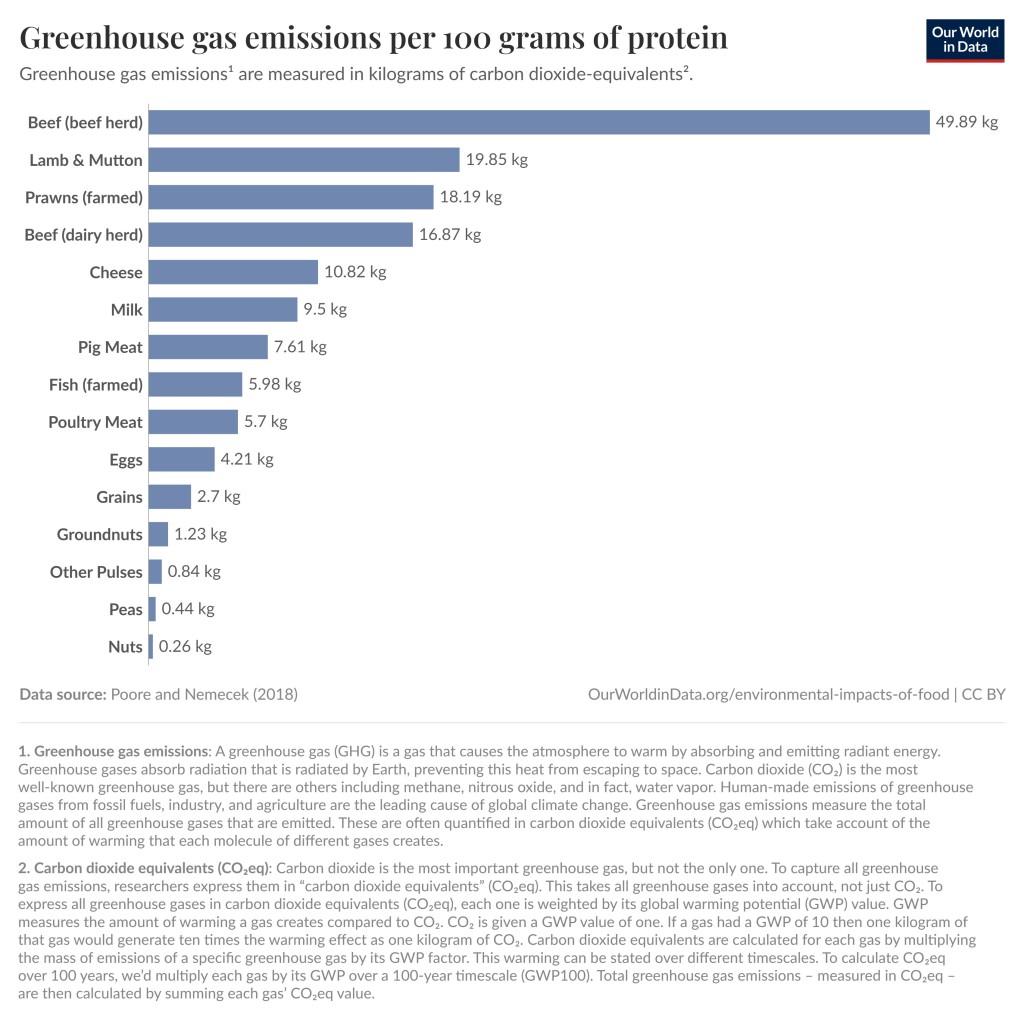
What really matters though is the type of food you eat, not whether it is organic or not. For example, beef (from beef herd) causes emissions 188 times larger than nuts do for the same amount of protein provided. Another thing to note is that if you eat 300 steaks per year you will have a 100 times larger environmental impact from your meat eating compared to someone who eats 3 steaks per year. You don’t have to become a vegetarian to have a smaller environmental impact but quantity matters.
Is Recycling Important?
The common perception that recycling is one of the best things you can do for the environment is not correct. Its impact is often not very large and if not done properly it can be counterproductive. If you throw a greasy pizza box in the recycling, you can ruin the entire batch.
Surveys across 21,000 adults in 30 countries showed that the two actions among twelve that people believed saved the most greenhouse gases were recycling (59%) and upgrading lightbulbs (36%). As it turns out, those two saved the least greenhouse gases among the twelve options. The option saving the most greenhouse gases among the 12 was giving up an SUV, which saved 18 times as much greenhouse gases as recycling. 17% of respondents picked that one.

According to Our World in Data (and the book Not the End of the World page 114<<Link-6>>), which is based on this research, giving up an average SUV for a sedan would save 3.6 metric ton, or 22.5% of the carbon emissions for the average American. Switching to a plant-based diet would save 2.2 metric ton per person, or 13.8%. Recycling comes in at a savings of 0.2 metric tons according to the same data. EPAs estimates are slightly higher but still low in comparison.
Plastic straws versus paper straws
Producing a plastic straw requires 39 kilojoules of energy and produces 1.5 grams of carbon dioxide emissions. However, producing a paper straw requires 96 kilojoules of energy and produces 4.1 grams of carbon dioxide emissions. So, plastic straws are better for the environment from that perspective. However, this could be compared to a typical passenger vehicle, which emits about 4.6 metric tons of CO2 per year according to EPA. That corresponds to more than 3 million plastic straws and more than one million paper straws.
According to the same article the average passenger vehicle emits about 400 grams of CO2 per mile. So, driving just one mile corresponds to hundreds of plastic straws and paper straws.


One advantage of paper straws is that they are easier to recycle, at least under ideal circumstances. Unfortunately, they often get soggy, and recycling plants don’t want that so they often throw them out. Another advantage is that paper straws decompose and don’t end up in our ocean.
However, not only are straws very small items, most of the plastic pollution in the ocean does not come from north America(1%) or Europe (1%). Paper straws versus plastic straws seem like a complex riddle but it may not be an important one. Whether you drive more or drive less is probably a lot more important.
Plastic bags versus paper bags
As with plastic straws versus paper straws plastic bags versus paper bags is a complicated question. From an environmental perspective they both have advantages and disadvantages. Plastic bags are less carbon intensive to produce, are easier to reuse several times, and the production of plastic bags require on average four times less energy than the production of paper bags.
On the other hand, paper bags are decomposable and easier to recycle. However, the chemicals and fertilizers used in producing paper bags create additional harm to the environment. It is a complicated question.

Having a Significant and Positive Impact on the Environment
Some of the allegedly sustainable practices and actions mentioned above are counter productive and others have a very small effect, for example, carbon emissions savings that are a few grams. According to the “Our World Data” and the book “Not the End of the World” page 114, a compilation of data research, some actions that you can take that will significantly reduce carbon emissions are (savings in metric tons per year, for flight it is per trip):
- Giving up an SUV 3.6 tons
- Go car free (average car) 2.4 tons
- Switch to plant-based diet 2.2 tons
- Avoid transatlantic flights 1.6 tons
- Buy green energy 1.5 tons
- Switch to electric car (from average sedan) 1.2 tons
- Switch from electric car to none 1.2 tons
- Avoid medium flight 0.6 tons (1,700 miles each way going and returning)
- Laundry in cold water 0.25 tons
- Hand-dry clothing 0.2 tons
- Recycle 0.2 tons
- Upgrade light bulbs 0.1 tons
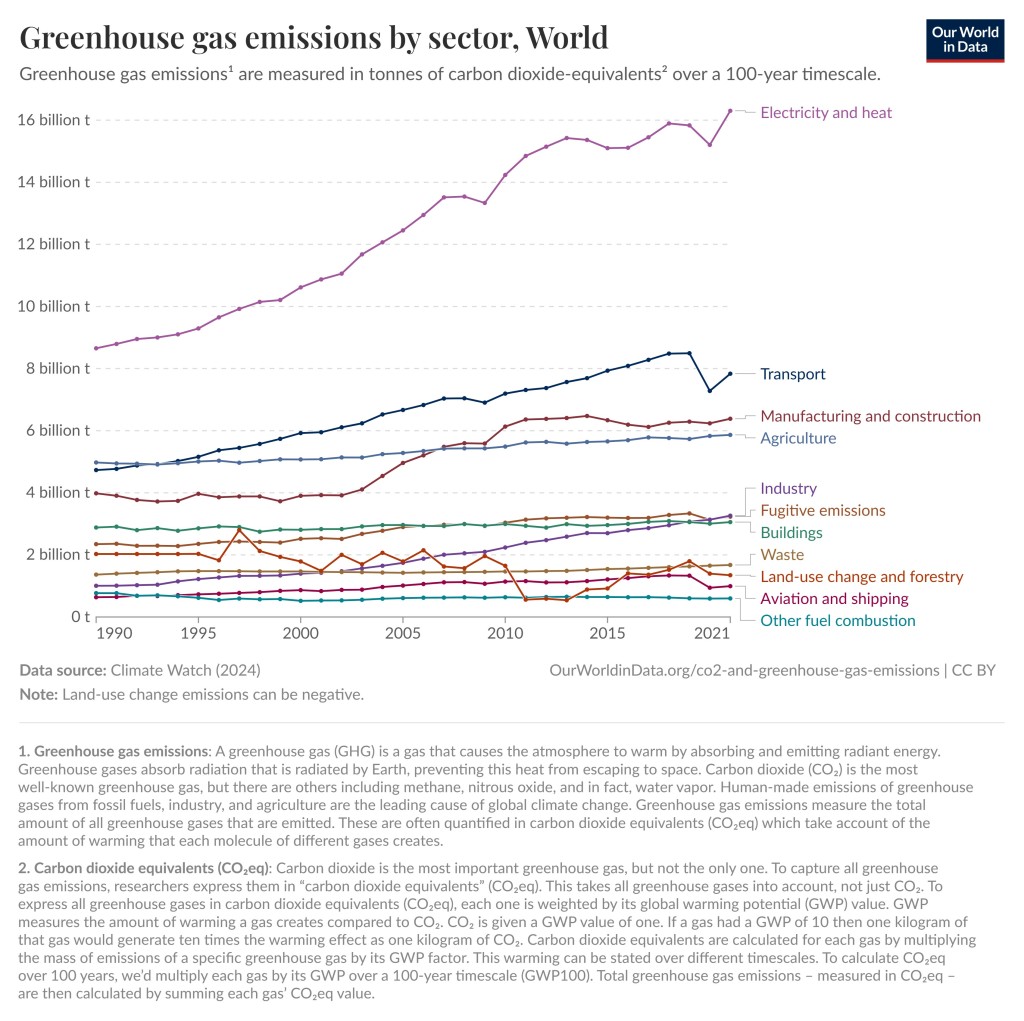
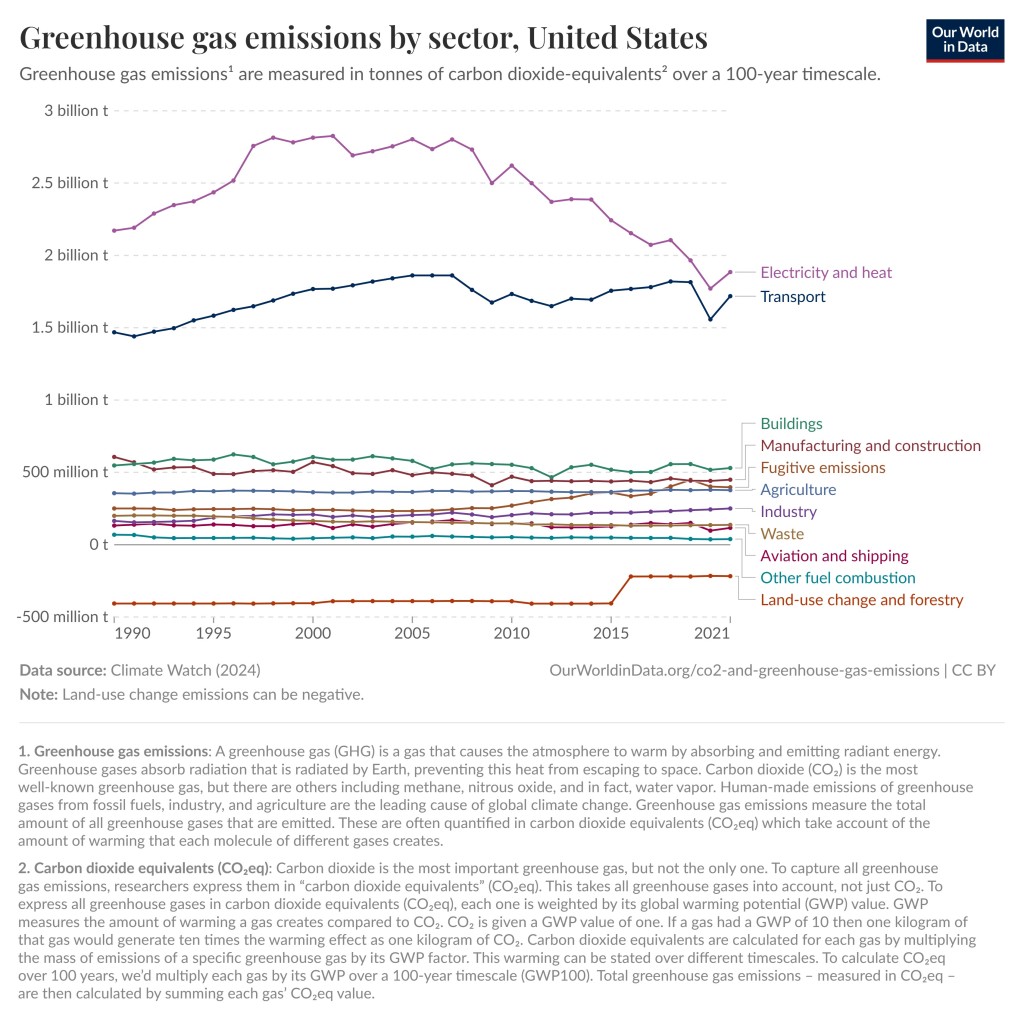
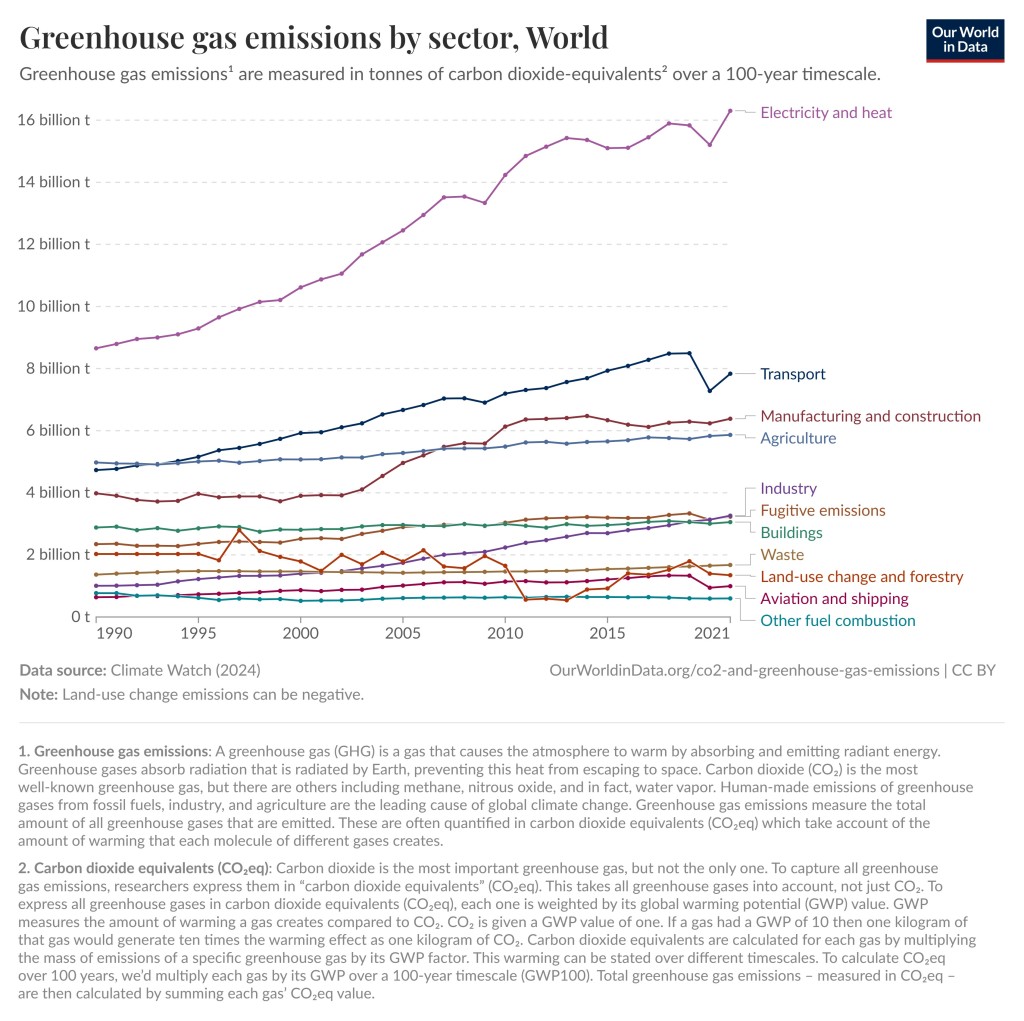
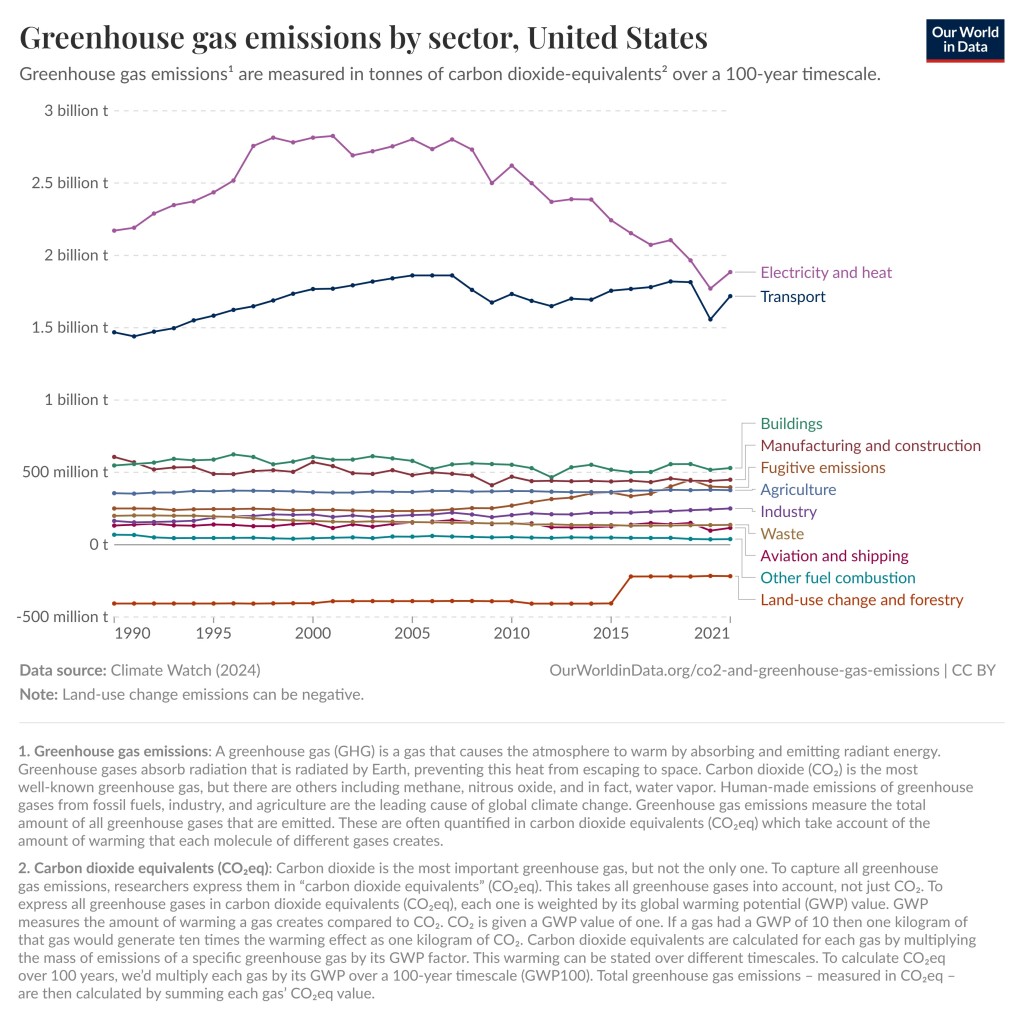
As you can see in the graphs below, the largest contributor of greenhouse gas emissions in the World and in the United States is electricity and heat. Unfortunately, the composition of the electric grid is something we as consumers have very little control over. We can save energy, get solar panels for our roof, or buy our electricity from green energy companies, but we cannot easily change the composition of the grid. Energy companies and politicians must do that.
However, we can make our voices heard by calling and writing to our representatives. This might be the single most impactful action that you as an individual can take. Your congressman, senator, or state legislator will probably not read your letter. They have hundreds of thousands or millions of constituents and get lots of letters every day. What is likely to happen is that a staff member will skim the letter and note the concern in a database.
Just make sure that your letter is politely written so it does not go in the wastebasket. Also make sure that you are a constituent. Writing to Ted Cruz when you live in Florida is not going to have an impact. They are interested in finding out what the concerns of their constituents are and according to staff members and other information I have come across, this really has an impact.
Conclusion
The survey mentioned above showed that among the twelve environmental actions an individual could take, the one with the second to smallest positive impact was the one that the majority thought had the biggest positive impact, despite it having a relatively tiny impact. The actions that could really make a huge difference were hardly considered.
We, the public, are very bad at determining what is good or bad for the environment and what has a significant and positive impact or not, even though the data is out there and we easily can look it up. Maybe the biggest positive impact one could have on the environment is to look up the facts and get better educated.