Super fact 31: The common perception that organic food is by default better for the environment or is an ideal way to reduce environmental impact is a misconception. Across several metrics, organic agriculture proves to be more harmful for the world’s environment than conventional agriculture.
There are things you can do as an individual to reduce your carbon footprint, use public transportation instead of driving, fly less, eat less read meat, don’t waste food, reduce your energy usage. There are straightforward actions you can take to reduce your use of water and avoid adding harmful pollution to the environment. However, as with eating locally grown food, eating organic food is often viewed as an environmentally friendly choice even though it often is not.
Organic farming is a method of growing food without using synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farming practices are intended to protect soil fertility, promote ecological balance, and reduce environmental impact. That’s all good. On the other hand, it should be noted that modern farming techniques, for example, using synthetic pesticides, have greatly increased cereal yield per acre and GMOs can reduce the use of toxic pesticides. It is complicated.
I consider this a super fact because it is often incorrectly assumed that eating organic food is the best choice for the environment.
Global Land Use
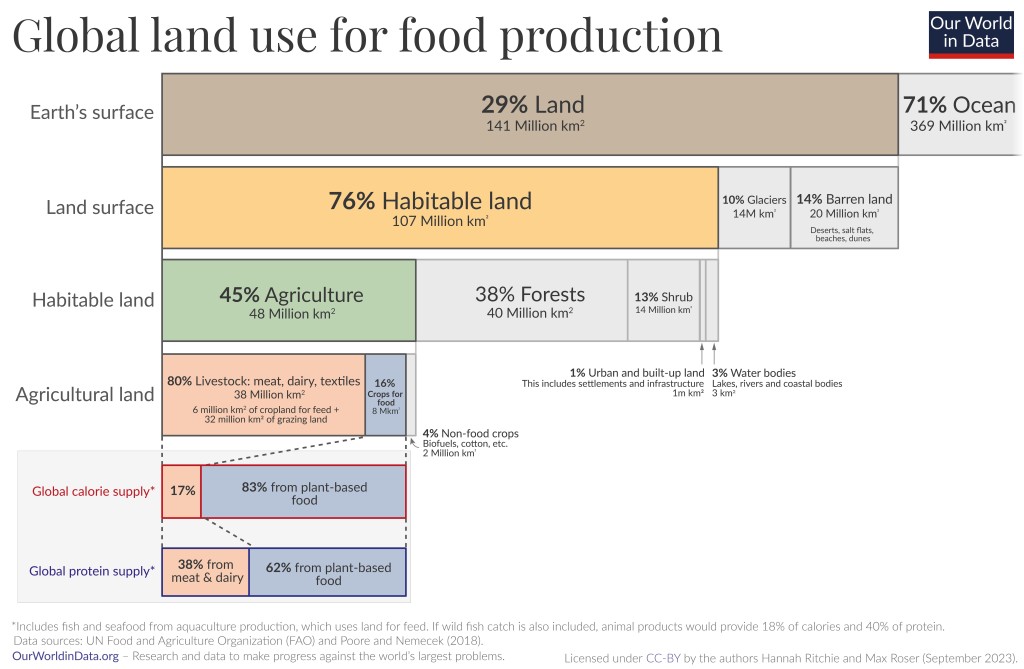
Before looking at the details of conventional farming versus organic farming lets look at global land use. In the figure below from Our World in Data you can see that agriculture already uses nearly half of all habitable land in the world. We cannot easily enlarge this percentage and therefore crop yield per acre is a very important factor to consider, and this is a great weakness for organic farming.
Also notice that 80% of agricultural land is used for livestock, meat, dairy and textile, but it only provides 17% global calorie supply. This second observation indicates that the type of food you eat may matter a lot more than whether it is produced via organic or conventional farming.
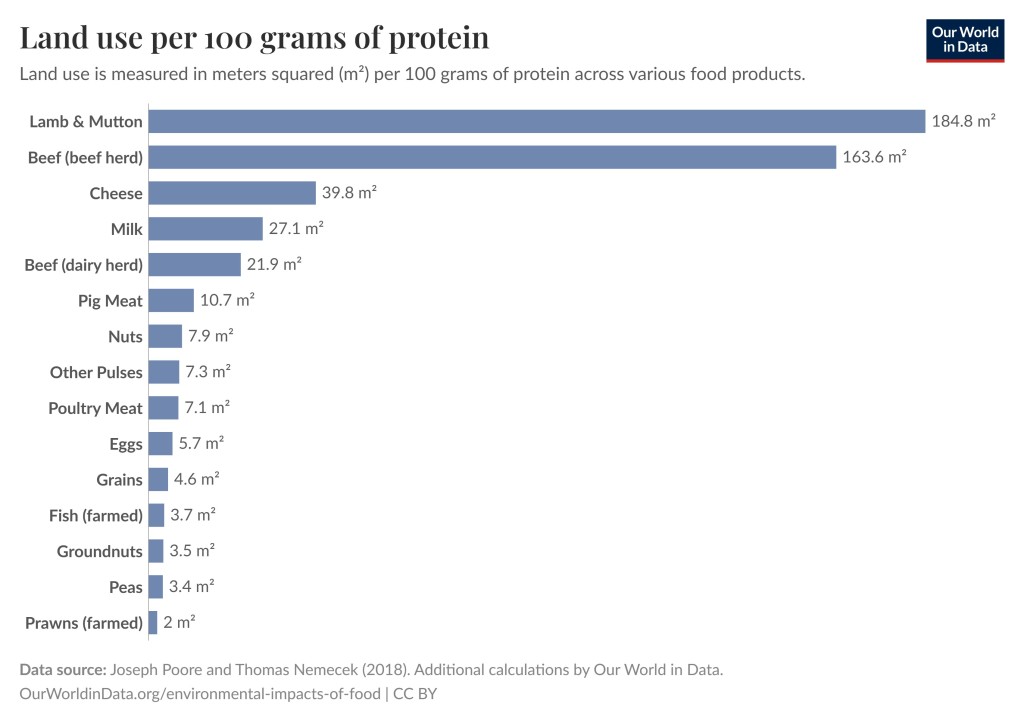
As you can see in the graph below, again from Our World in Data, the land used for producing 100 grams of protein varies enormously between different food groups. 100 grams of protein from lamb and mutton require on average 52.8 times as much land as 100 grams of protein from groundnuts. This graph does not make a distinction between organic farming and conventional farming, but it highlights the huge difference between different food sources. I’ll get to the difference between organic farming and conventional farming with respect to land use later in the post.
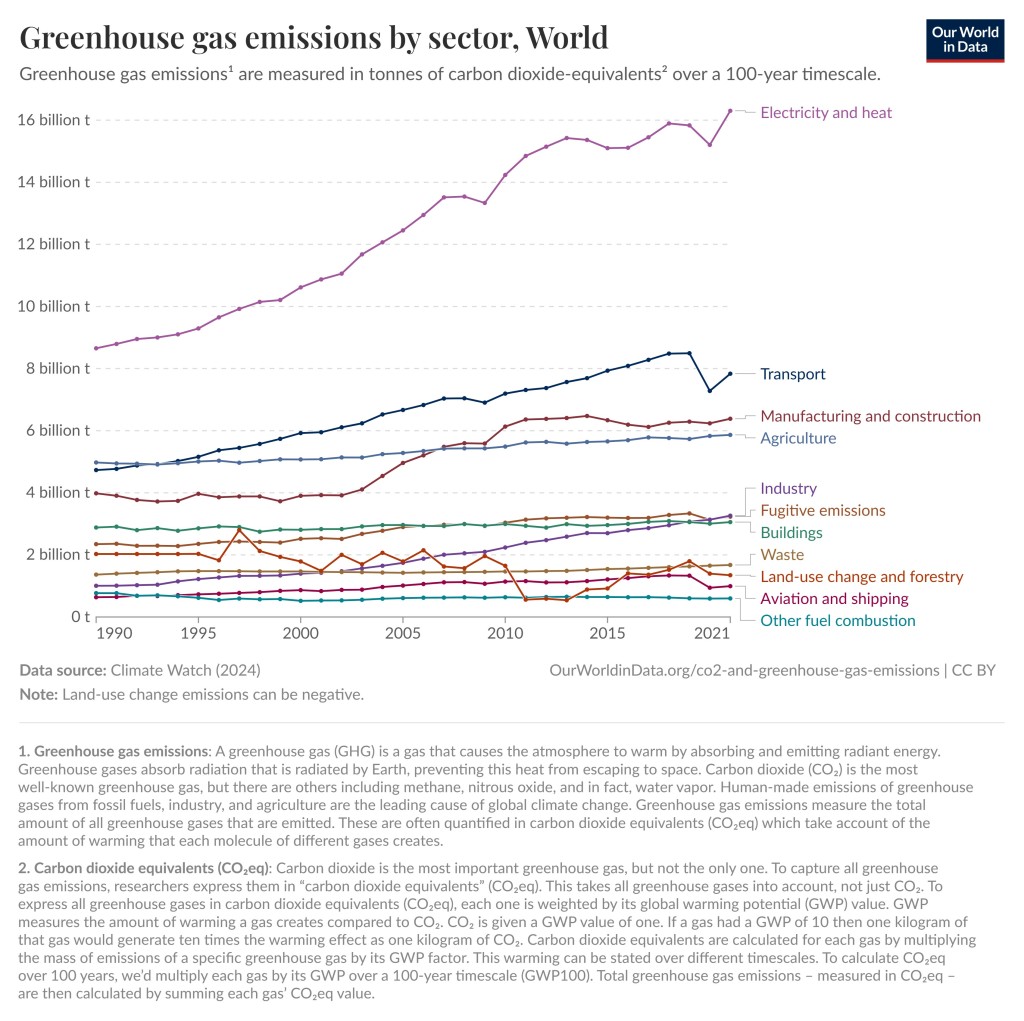
Agriculture and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
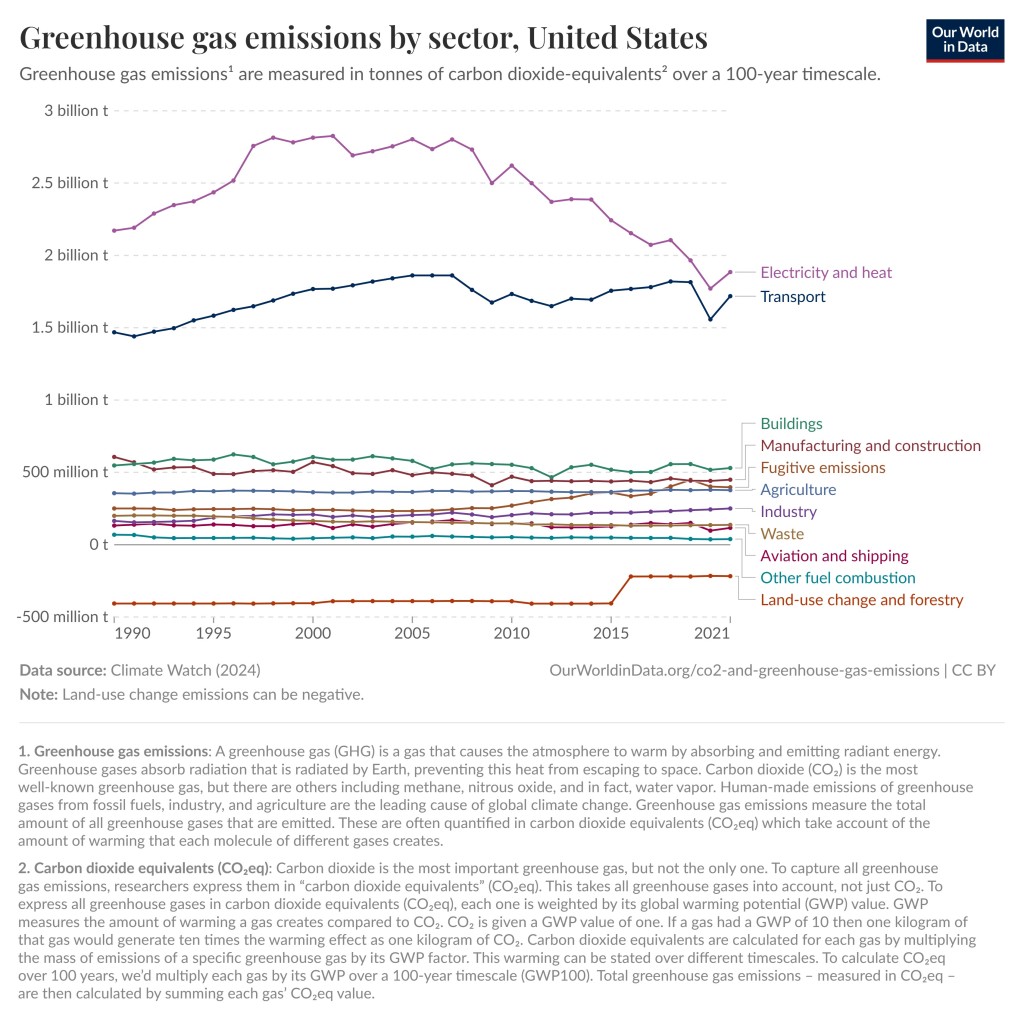
The next two graphs focus on the greenhouse gas emissions including those from agriculture. Electricity and Transport dominate both globally and in the United States, but globally agriculture comes in at 6 billion of the 40 billion tons of greenhouse gas emissions for 2021, which is 15%. For the United States agriculture comes in at 10.6% of greenhouse gas emissions for 2021. In other words, agriculture was not the largest contributor of greenhouse gas emissions but still an important factor.
Finally, the contribution for different types of food. Notice that beef (beef herd) at 49.89kg is 188 times larger than the 0.26kg for nuts. 188 people eating nuts contribute as much to carbon emissions as one person eating beef.
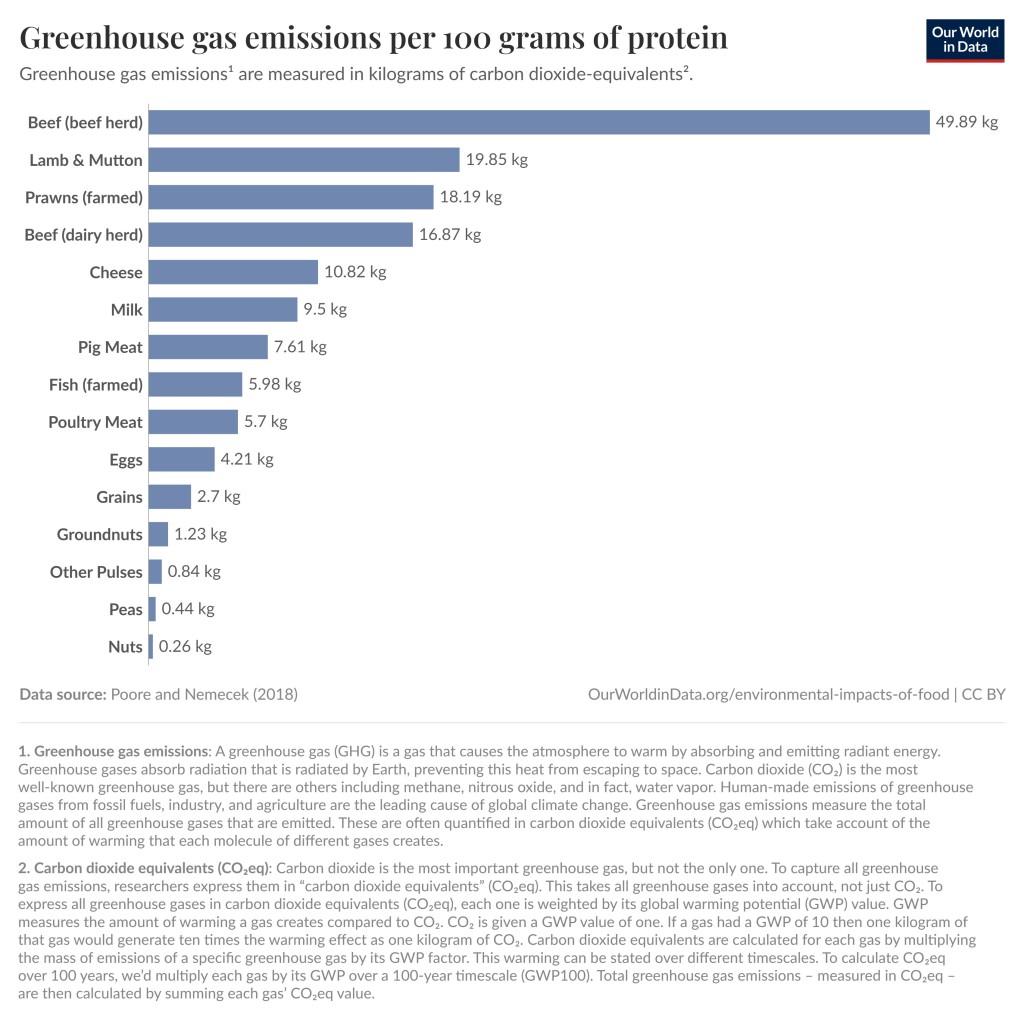
Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2eq)
Carbon dioxide is the most important greenhouse gas, but not the only one. To capture all greenhouse gas emissions, researchers express them in “carbon dioxide equivalents” (CO2eq). This takes all greenhouse gases into account, not just CO2. To express all greenhouse gases in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2eq), each one is weighed by its global warming potential (GWP) value. GWP measures the amount of warming a gas creates compared to CO2. CO2 is given a GWP value of one.
If a gas had a GWP of 10 then one kilogram of that gas would generate ten times the warming effect as one kilogram of CO2. Carbon dioxide equivalents are calculated for each gas by multiplying the mass of emissions of a specific gas by its GWP factor. This warming can be stated over different timescales. To calculate CO2eq over 100 years, we’d multiply each gas by its GWP over a 100-year timescale (GWP100). Total greenhouse gas emissions – measured in CO2eq – are then calculated by summing each gas’ CO2eq value.
Environmental Impact of Organic Versus Conventional Agriculture
At this point it should be clear that eating different types of food, nuts and vegetables versus red meat makes huge difference regarding the environment. How about organic versus conventional farming? Well, it is complicated. You have to take into account land use, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity, pesticide application, energy use and more.
Clark and Tilman (2017) published a meta-analysis of results of published organic-conventional comparisons across 742 agricultural systems over 90 unique foods. The food groups consisted of cereals, pulses and oil crops, fruits, vegetables, dairy and eggs, and meats. As you can see in the resulting graph below organic agriculture is worse for the environment for most food groups with regards to land use, eutrophication potential, and acidification potential. The result is mixed with respect to greenhouse gas emissions and energy use.
It appears that it is best to choose organic pulses and fruits and choose non-organic for all other food products (cereals, vegetables, dairy and eggs, and meat). However, if your primary concern is whether the potato accompanying your steak is conventionally or organically produced, then your focus is arguably misplaced. Whether you go organic or non-organic the steak is much worse for the environment.

Conclusion
In this post I present empirical evidence from reliable sources comparing organic to conventional agriculture in terms of environmental impact. Despite strong public perception of organic agriculture producing better environmental outcomes, conventional agriculture often performs better on environmental measures including land use, greenhouse gas emissions, and pollution of water bodies. There are, however, some contexts where organic agriculture may be better for the environment. In short it is complicated.
What really matters though is the type of food you eat, not whether it is organic or not. Another thing to note is that if you eat 300 steaks per year you will have a 100 times larger environmental impact compared to someone who eats 3 steaks per year. Quantity matters. This post was about environmental impacts. There are other considerations such as health, what you like, whom you want to support, etc.













